When it comes to lowering your carbon footprint, choosing a more eco-friendly mode of transportation is a decision that can have a positive impact on the environment.
While there are a variety of eco-friendly transportation options, one of the more popular options is an electric vehicle. Because they have no tail-pipe emissions, EVs are typically responsible for lower levels of greenhouse gases than an average new gasoline car.
And with a recent rise in popularity, more car brands have begun designing their own EVs and body styles range from sedans to trucks and much in between.
But before deciding whether an EV is right for you, it helps to understand a bit more about how they work. We dig into the differences between EVs and gasoline-powered vehicles, types of EVs, and pros and cons to consider.
How Do Electric Cars Work?
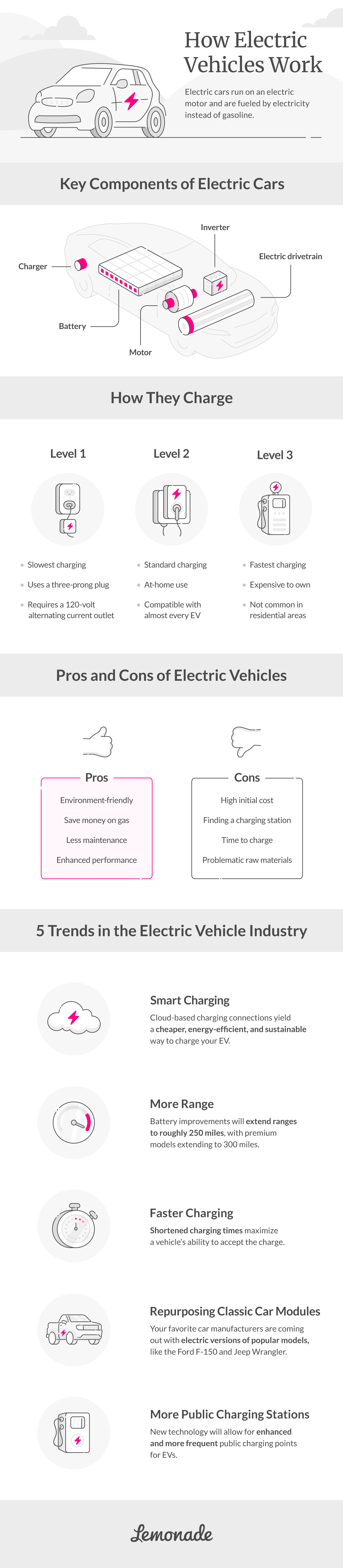
If you’ve ever wondered how electric vehicles work, the answer is pretty simple. EVs are powered by a battery that stores electricity to power the motor. To be recharged, all you have to do is plug the car into a compatible charger.
Electric cars are fully powered by electricity whereas hybrid cars run on a combination of electricity and conventional fuel.
EVs can only go so many miles before they need to be recharged. On average, EVs can run for 250 miles per charge.
Because these cars don’t include an internal combustion engine, EVs are much quieter vehicles. This often surprises new EV drivers when they make the switch from a traditional car to an electric.
Types of Electric Vehicles
There are four main types of electric cars: battery electric vehicle (BEV), plug-in hybrid electric vehicle (PHEV), hybrid electric vehicle (HEV), and hydrogen electric vehicles (fuel cell).
- BEV: A BEV is a fully electric car that runs entirely on electricity.
- PHEV: A PHEV sports an internal combustion engine (ICE) that allows you to switch from running on electricity or fuel. A PHEV can operate on gasoline alone if the electric battery isn’t charged, or they can use the battery charge if they run out of fuel.
- HEV: A hybrid electric vehicle (HEV) uses a combination of fuel and electricity. Unlike PHEVs, HEVs can only top off with traditional fuel and cannot be recharged like PHEVs and BEVs.
- Fuel cell: The fuel cell electric vehicles create their own energy through a chemical reaction with the use of hydrogen. These cars can be filled with hydrogen and do not require a standard charging system for electricity.
Advantages and Disadvantages of EVs
While EVs boast many advantages, there are a few factors to consider before you make the switch from a traditional car to an electric one.
Advantages:
- They’re eco-friendly: EVs boast zero emissions, which helps to reduce the amount of smog and greenhouse gases that your vehicle emits into the atmosphere.
- They save you money on gas: With the price of gasoline rising, you’ll be able to save money and time by skipping the gas station altogether. EV owners can expect to pay up to half the price for power charging than they would to fuel a gas-powered car.
- They require less maintenance: Say goodbye to oil changes and oil filter changes. Your EV has fewer parts than a traditional car and because it doesn’t run on gasoline, you won’t need to worry about some of those routine maintenance considerations.
- They’re high-performance vehicles: EVs boast quick acceleration and can reach peak speeds in just a few seconds.
Disadvantages:
- They might not be the best for road trippers: For drivers that often go long distances in their cars, EVs might not be ideal because, on average, EVs need to be recharged every 250 miles. Plus, it can take hours to charge your EV fully.
- They can have a high initial cost: Electric cars cost less to operate and maintain, but they often come with a high sticker price. However, there are options to help lower the cost such as looking into whether you qualify for a federal tax credit.
- It can be hard to find a charging station: Even if you plan ahead, you could come across a charging station that’s broken or that has a non-EV parked in the station’s spot.
- They require raw materials that can create carbon pollution: While EVs are eco-friendly in the way that they run, the materials necessary to create an EV can contribute to carbon pollution. This is because EVs use lithium ion cells to power their batteries, which are made of mined materials. Extracting the metals requires the use of smelting, which can emit harmful air pollutants like sulfur oxide.
While electric vehicles aren’t for everyone, new technologies and body types are making them a more enticing option for many drivers.
It’s important to factor in both the pros and cons of EVs into your decision, as certain lifestyles and driving habits may make buying an EV more of a no-brainer for some. If you’re not quite ready to make the leap to an EV, there are eco-friendly car features to look for in a potential new ride.
Whether or not you decide to go the EV route, you can expect to see more of these vehicles on the road in recent years, as governments offer tax credits and incentives to help reduce our carbon footprint.
Please include attribution to Lemonade.com with this graphic.